Solar Energy Risks That Could Impact Your Investment (And How to Protect It)

Safeguarding your solar energy investment requires understanding both technical and financial vulnerabilities in today’s rapidly evolving renewable energy landscape. While solar technology offers remarkable returns, investors face specific challenges: equipment degradation can reduce system efficiency by up to 20% over time, extreme weather events pose increasing threats to installations across Europe, and regulatory changes may impact feed-in tariffs and incentive programs. Modern solar projects must navigate cybersecurity concerns, with smart monitoring systems becoming potential entry points for malicious attacks.
Yet these risks shouldn’t deter adoption – they demand strategic management. Professional risk assessment protocols, comprehensive insurance coverage, and advanced monitoring systems now offer robust protection for solar assets. European markets have developed sophisticated risk mitigation tools, from performance guarantee insurance to weather derivatives, enabling investors to secure their renewable energy future with confidence.
By identifying and addressing these challenges early, stakeholders can maximize system longevity while maintaining optimal performance levels. This proactive approach to risk management has become essential for sustainable solar energy development across residential and commercial sectors.
Physical Risks to Solar Installations
Weather-Related Damage
Weather-related incidents pose significant challenges for solar energy systems across Europe. Severe storms, hail, and extreme weather conditions can potentially impact both the performance and longevity of solar installations. Hailstorms present a particular concern, with large hailstones capable of causing physical damage to solar panels, though modern panels undergo rigorous testing to withstand impacts from hailstones up to 25mm in diameter.
Heavy snow accumulation can reduce energy production and, in extreme cases, cause structural stress on mounting systems. However, most contemporary installations are designed with sufficient tilt angles to facilitate natural snow sliding, while robust mounting frameworks are engineered to handle additional snow loads common in Alpine regions.
Strong winds pose another significant risk, particularly for roof-mounted systems. Wind uplift forces can stress mounting equipment and, in extreme cases, compromise panel attachment points. This risk is effectively mitigated through proper installation techniques and adherence to local wind load requirements during the design phase.
Lightning strikes, though rare, can cause substantial damage to solar systems and associated electrical components. The installation of proper surge protection devices and adequate grounding systems is essential for protecting against such events.
To safeguard against weather-related damages, investors should:
– Ensure installations meet regional weather resistance standards
– Install comprehensive monitoring systems
– Maintain adequate insurance coverage
– Schedule regular professional inspections
– Document all weather-related incidents for warranty claims
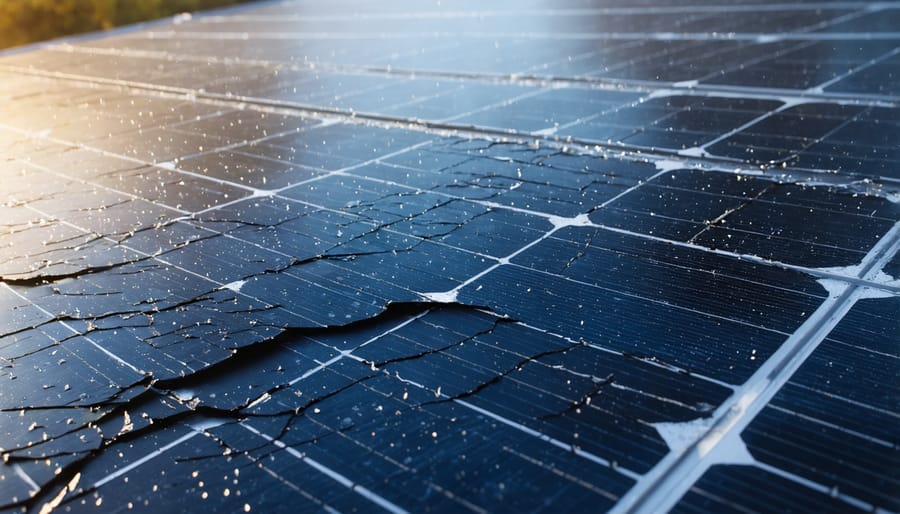

Equipment Degradation and Failure
Solar panels and associated equipment, while generally reliable, can experience various forms of degradation and failure throughout their operational lifetime. Natural wear occurs gradually, with most quality solar panels showing a performance decline of 0.5% to 1% annually. This degradation primarily results from exposure to UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and weather extremes common across European climates.
Manufacturing defects, though relatively rare in certified equipment, can manifest as micro-cracks, delamination, or faulty connections. These issues might not be immediately apparent but can significantly impact system performance over time. Hot spots, which occur when cells operate at higher temperatures than surrounding areas, can accelerate degradation and potentially cause irreversible damage to panels.
Inverters, essential components in solar installations, typically have shorter lifespans than panels and may require replacement after 10-15 years. Performance issues can also arise from degraded wiring, loose connections, or corroded components, particularly in regions with high humidity or maritime environments.
Regular maintenance and monitoring can help identify these issues early. Quality assurance begins with selecting certified equipment from reputable manufacturers and continues through professional installation and periodic inspections. Modern monitoring systems can detect performance drops and component failures before they lead to significant energy production losses, enabling proactive maintenance and protecting your solar investment.
Financial and Operational Risks
Performance and Output Risks
Performance and output risks represent significant concerns for solar energy systems, directly impacting their financial viability and return on investment. Weather variability plays a crucial role, as cloudy conditions, seasonal changes, and unexpected weather patterns can reduce energy production below projected levels. In Northern European regions, where solar irradiance varies significantly throughout the year, this risk becomes particularly relevant.
System degradation is another key factor affecting performance. While modern solar panels typically guarantee 80% performance after 25 years, various environmental factors can accelerate degradation. These include pollution, dust accumulation, and extreme temperature fluctuations common across European climates. Regular maintenance becomes essential to mitigate these risks and maintain optimal efficiency.
Technical issues can also impact output levels. Inverter failures, wiring problems, or module defects may lead to system underperformance or complete shutdowns. These challenges directly affect revenue streams, especially for commercial installations where production guarantees may be in place.
To protect against these risks, implementing robust monitoring systems is crucial. These solutions provide real-time performance data and early warning signals for potential issues. Additionally, proper system design that accounts for local climate conditions and includes redundancy measures can help maintain consistent output levels.
Insurance solutions specifically designed for solar installations can offer financial protection against performance shortfalls. Many European providers now offer performance guarantee insurance, helping stakeholders safeguard their investments against unexpected output reductions.
Regular professional assessments and maintenance schedules, combined with weather forecasting tools, can help operators anticipate and manage performance variations, ensuring more stable and predictable energy production over the system’s lifetime.
Market and Regulatory Changes
The solar energy landscape is continuously shaped by evolving market dynamics and regulatory frameworks across Europe. One of the most significant risks for solar energy investors lies in the unpredictability of policy changes and incentive programs. Understanding solar regulations and compliance requirements is crucial for long-term project success.
Feed-in tariffs, which once drove significant solar adoption, have seen substantial modifications in several European countries. These changes can directly impact return on investment calculations and project viability. Similarly, shifts in renewable energy certificates (RECs) and carbon credit markets create additional layers of financial uncertainty.
Market fluctuations also pose considerable risks. Supply chain disruptions, particularly in photovoltaic component manufacturing, can lead to price volatility and delivery delays. The recent global events have highlighted the vulnerability of international supply networks and their impact on project costs.
Local building codes and grid connection requirements frequently undergo updates, potentially necessitating design modifications or additional investments. Smart investors maintain close relationships with regulatory bodies and industry associations to stay ahead of pending changes.
To mitigate these risks, stakeholders should:
– Develop flexible business models that can adapt to policy changes
– Diversify supply chain partnerships
– Build contingency buffers into project timelines and budgets
– Regularly review and update compliance strategies
– Engage with industry experts for regulatory guidance
The key to successful solar energy investment lies in maintaining awareness of market trends while establishing robust risk management strategies that can weather regulatory shifts and market volatility.
Essential Risk Management Strategies
Insurance Solutions
The insurance market offers a range of specialized products designed to protect solar energy investments across Europe. Property insurance forms the foundation, covering physical damage to solar panels and associated equipment from events like storms, fires, and vandalism. For larger installations, Construction All Risk (CAR) insurance provides comprehensive coverage during the installation phase, while Operational All Risk (OAR) policies protect against revenue losses during operation.
Performance ratio insurance has emerged as a crucial product, safeguarding against underperformance of solar systems. This coverage compensates owners when energy generation falls below guaranteed levels due to technical issues or unexpected environmental conditions. Weather index insurance offers protection against revenue losses caused by below-average solar irradiation, particularly relevant in regions with variable climate patterns.
Business interruption insurance helps recover lost income during system downtime, while liability insurance protects against third-party claims. For commercial installations, specialized products like serial defect coverage and degradation performance coverage ensure long-term protection against manufacturing defects and gradual efficiency loss.
Many insurers now offer bundled solutions combining multiple coverage types, tailored to specific project sizes and risk profiles. These comprehensive packages often include additional services like risk assessment, monitoring, and claims support, providing peace of mind for both residential and commercial solar investments. Working with experienced insurance brokers who understand the solar energy sector can help identify the most appropriate coverage options for your specific needs.
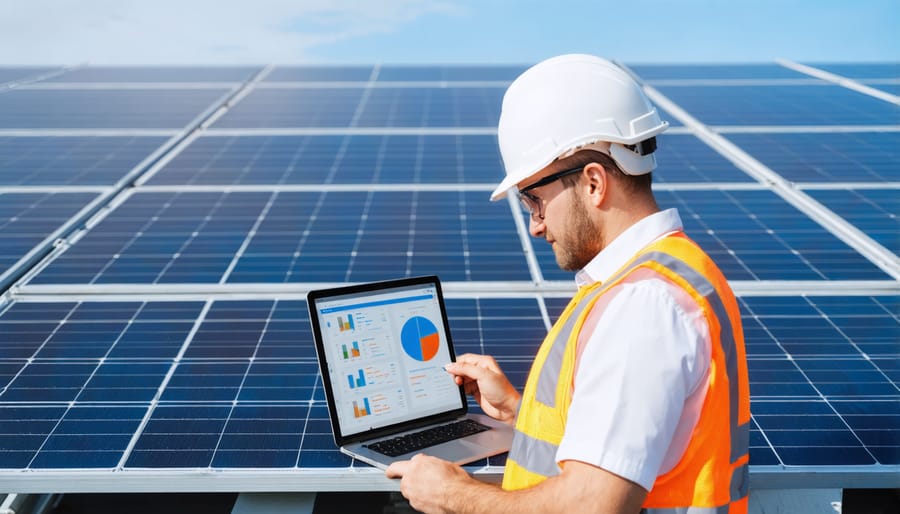
Technical Risk Mitigation
Implementing robust monitoring systems and quality standards is crucial for minimizing technical risks in solar energy installations. Modern solar facilities benefit from advanced monitoring technologies that provide real-time performance data and early warning signals for potential issues. These systems can detect everything from minor efficiency drops to critical component failures, enabling proactive intervention before problems escalate.
Regular adherence to solar maintenance protocols is essential for maintaining optimal system performance and longevity. This includes routine inspections of panels, inverters, and mounting structures, along with periodic cleaning and performance testing. Quality standards certification, such as IEC 61215 for PV modules and IEC 62446 for system documentation, ensures that installations meet European safety and performance requirements.
Smart inverter technology plays a vital role in risk mitigation by providing surge protection and grid stability features. Advanced monitoring platforms can integrate weather forecasting data to optimize system performance and protect against environmental stresses. Additionally, thermal imaging and electroluminescence testing help identify potential hot spots or micro-cracks before they become serious issues.
For maximum protection, implementing a comprehensive maintenance strategy that combines automated monitoring with scheduled physical inspections is recommended. This dual approach ensures both immediate issue detection and long-term system reliability, ultimately safeguarding your solar investment.

Financial Protection Measures
Implementing robust financial protection strategies is crucial when investing in solar energy systems. Start by securing comprehensive warranties that cover both equipment and performance guarantees. Most quality solar panels come with 25-year performance warranties, while inverters typically offer 10-15 year coverage. Ensure these warranties are backed by financially stable manufacturers with established European presence.
Insurance coverage specifically designed for solar installations provides additional security against unexpected damages, theft, or system failures. Many European insurers now offer specialised policies that protect both the physical infrastructure and potential revenue loss from system downtime.
Performance contracts and production guarantees can safeguard your expected energy yields. These agreements typically specify minimum generation levels and include compensation mechanisms if targets aren’t met. Consider working with installers who offer monitoring services and maintenance contracts to ensure optimal system performance.
For commercial installations, power purchase agreements (PPAs) can provide stable revenue streams while minimising upfront costs. These contracts should include clear terms regarding pricing, duration, and maintenance responsibilities. Additionally, exploring green certificates and renewable energy incentives can help offset initial investments and provide long-term financial benefits.
Always engage legal experts familiar with renewable energy contracts to review documentation before signing. This ensures your interests are protected and all contractual obligations are clearly defined.
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive analysis, solar energy presents both significant opportunities and notable risks that require careful consideration and management. The successful implementation of solar projects across Europe depends heavily on understanding and mitigating these various risk factors, from technical challenges to financial considerations.
The key to maximizing solar energy benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks lies in adopting a holistic risk management approach. This includes conducting thorough site assessments, implementing robust maintenance protocols, securing appropriate insurance coverage, and working with qualified professionals throughout the project lifecycle. European homeowners and businesses can significantly reduce their exposure to common risks by following industry best practices and staying informed about technological developments and regulatory changes.
Weather-related challenges, equipment degradation, and financial uncertainties remain important considerations, but these shouldn’t deter potential solar adopters. Instead, they should serve as motivators for better planning and risk mitigation strategies. The solar energy sector continues to evolve, with improving technologies and growing expertise in risk management making solar installations increasingly reliable and cost-effective.
For European stakeholders, the path forward involves balancing innovation with prudence. This means embracing new solar technologies while maintaining realistic expectations about system performance and return on investment. Working with certified installers, maintaining comprehensive documentation, and establishing clear maintenance schedules are essential steps in protecting solar investments.
As the solar energy market matures, we’re seeing more sophisticated risk management tools and services becoming available. These resources, combined with growing industry experience and improved regulatory frameworks, provide a solid foundation for successful solar energy adoption.
Remember that while risks cannot be eliminated entirely, they can be effectively managed through proper planning, regular maintenance, and proactive monitoring. By understanding and addressing potential risks early in the project lifecycle, stakeholders can ensure their solar investments deliver long-term value while contributing to Europe’s sustainable energy future.
Leave a Reply