Smart Solar Farming: How a 1-Acre Solar Setup Powers Modern Agriculture
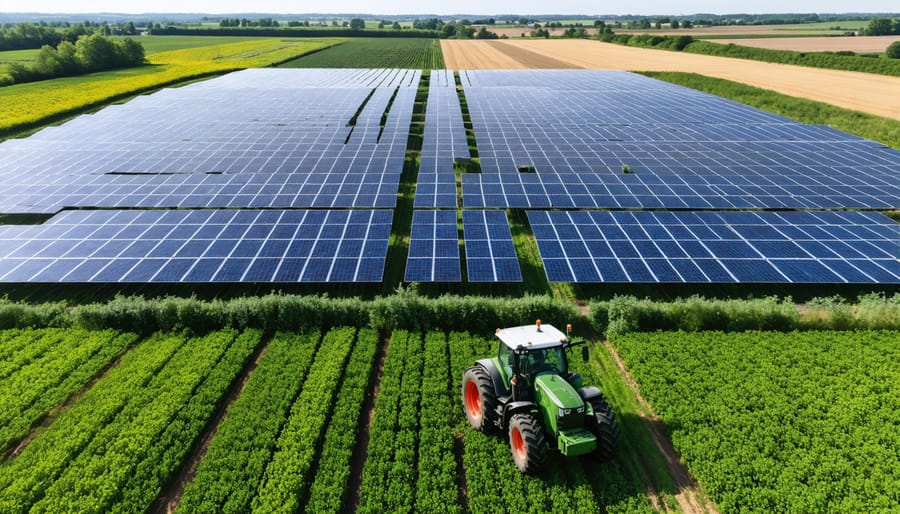

Transform a single acre into a powerful clean energy generator capable of producing up to 150,000 kWh annually – enough to power 40 European households while maintaining agricultural productivity. Solar farms represent the perfect fusion of modern energy innovation and traditional farming practices, particularly across Europe’s diverse agricultural landscape. A one-acre solar installation requires approximately 4,000 square meters of land, accommodating roughly 400 solar panels configured in optimal east-west orientation for maximum energy harvesting. These dual-purpose installations, increasingly common in countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands, enable farmers to generate sustainable income through energy production while continuing crop cultivation or grazing beneath the elevated panels. The strategic implementation of agrivoltaic systems addresses two critical challenges simultaneously: meeting Europe’s ambitious renewable energy targets and preserving valuable agricultural land, making one-acre solar farms an increasingly attractive investment for forward-thinking landowners and agricultural enterprises.
Planning Your 1-Acre Solar Farm for Agricultural Use
Space Requirements and Layout Optimization
A one-acre solar farm requires careful spatial planning to maximise energy generation potential. Typically, a one-acre plot (approximately 4,047 square meters) can accommodate between 350 to 450 solar panels, depending on panel size and configuration. The optimal layout generally allows for 2-meter spacing between panel rows to prevent shading and ensure maintenance access.
For maximum efficiency, panels should be arranged in south-facing rows (in the Northern Hemisphere) with a tilt angle between 30-40 degrees, depending on the specific location within Europe. This configuration typically requires about 70% of the available land area, leaving the remaining space for access roads, inverter stations, and maintenance pathways.
Key spatial considerations include:
– Panel dimensions (typically 1.7m × 1m)
– Inter-row spacing (minimum 2m)
– Maintenance corridors (3m wide)
– Equipment housing (approximately 15-20 square meters)
– Security fencing perimeter (1m inside property boundary)
Modern design software helps optimise panel placement while accounting for site-specific factors like terrain variations and local shading obstacles. This precise planning ensures maximum energy yield while maintaining system accessibility and longevity.
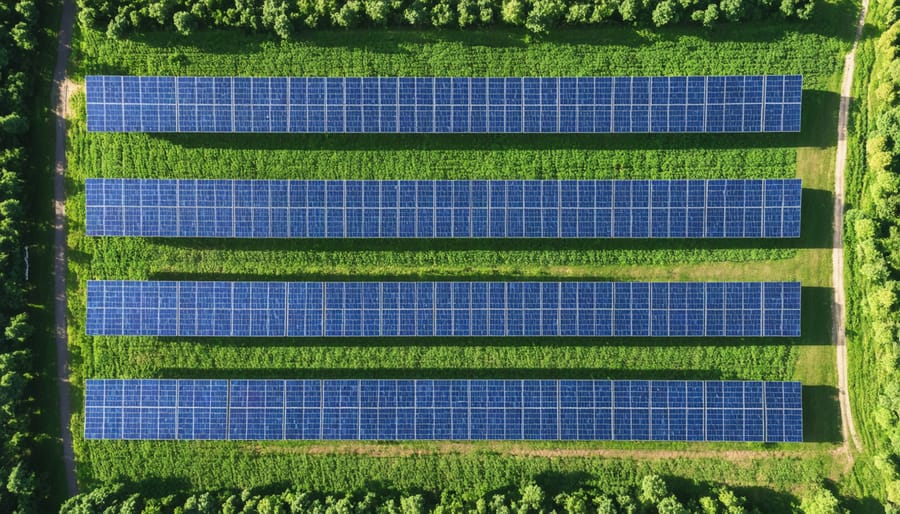

Equipment Selection and Power Output Potential
A typical 1-acre solar farm requires approximately 400-435 solar panels, depending on panel efficiency and layout optimization. Modern monocrystalline panels, rated between 400-550W each, are recommended for maximum space utilization. Essential equipment includes robust mounting systems, inverters (string or central), and smart PV monitoring systems for optimal performance tracking.
With current technology, a well-designed 1-acre installation can generate between 200-250 kW of power under ideal conditions. This translates to approximately 350-430 MWh of electricity annually in most European regions, accounting for seasonal variations and typical weather patterns. The exact output depends on factors such as geographical location, panel tilt angle, and local solar irradiance levels.
Critical components also include electrical safety equipment, transformers for grid connection, and weather-resistant cabling. Modern installations increasingly incorporate bifacial panels, which can increase energy yield by 5-15% by capturing reflected light, making them particularly effective in snow-covered regions or areas with high ground reflectivity.
Dual-Use Agricultural Applications
Crop Integration Strategies
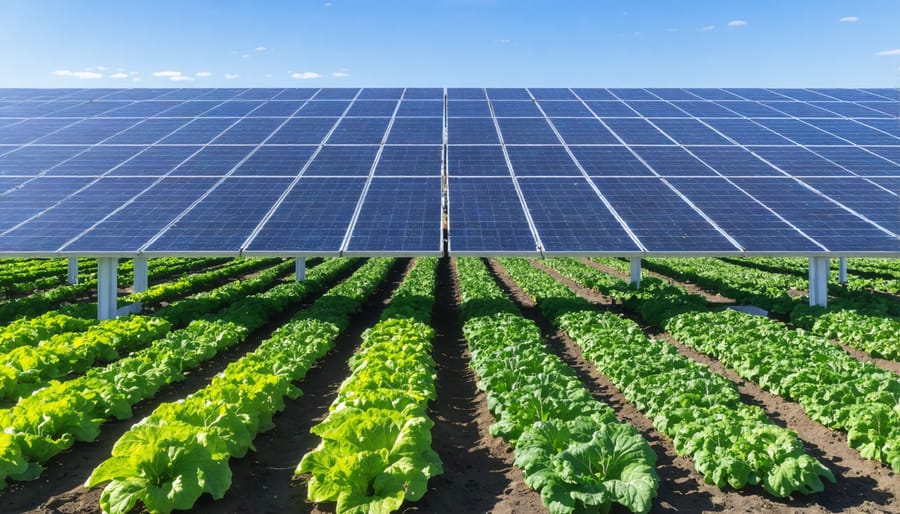
Modern solar agrivoltaics have revolutionised the way we approach land use in solar farming. By carefully selecting compatible crops and implementing smart spacing strategies, farmers can maintain agricultural productivity while generating clean energy.
Low-growing crops like lettuce, spinach, and certain herbs thrive particularly well under elevated solar panels, benefiting from the partial shade they provide. The panels’ height is typically adjusted to 2.5-3 metres, allowing standard farming machinery to operate underneath while ensuring optimal light distribution for both energy generation and plant growth.
Innovative mounting systems enable panels to be positioned at specific angles or with wider spacing, creating light corridors that support diverse crop rotation patterns. Some installations incorporate automated tracking systems that adjust panel positions throughout the day, optimising both solar exposure and crop requirements.
Water management becomes more efficient in these integrated systems, as solar panels help reduce evaporation and protect crops from extreme weather conditions. Many European farmers have successfully implemented drip irrigation systems that work in harmony with the panel layout, ensuring uniform water distribution.
For optimal results, seasonal crop planning should align with solar panel maintenance schedules, minimising any potential disruption to either operation. This dual-use approach not only maximises land efficiency but also contributes to sustainable farming practices across Europe.

Livestock Management Solutions
Integrating livestock management with solar installations, known as agrivoltaics, offers a dual-purpose solution for land utilisation. Sheep grazing has proven particularly successful in European solar farms, as these animals naturally maintain vegetation height without damaging solar equipment. A typical 1-acre solar installation can support 3-4 sheep, providing sustainable grass management while generating additional revenue streams.
The practice requires careful planning and specific adaptations to the solar array design. Panels should be installed at a minimum height of 1.5 metres to allow comfortable animal movement underneath. Protective measures for cables and electrical components are essential, typically involving robust conduit systems and raised junction boxes.
Different livestock species offer varying benefits. While sheep are the most common choice, some installations successfully incorporate poultry, particularly for pest control. These birds help manage insects and reduce the need for chemical treatments around solar equipment.
To implement a successful livestock management programme, consider:
– Installing appropriate fencing systems
– Creating designated water access points
– Establishing rotational grazing patterns
– Monitoring vegetation quality and growth
– Maintaining regular veterinary care schedules
Working with local shepherds or agricultural cooperatives can provide expertise in animal management while sharing operational costs. This integration not only maintains the solar farm’s efficiency but also contributes to biodiversity and soil health, making it an environmentally sound investment for European solar developers.
Economic Benefits and ROI Analysis
Energy Cost Savings
A 1-acre solar farm can generate substantial cost savings through reduced electricity expenses and potential revenue streams. Based on current European energy rates, a well-designed solar installation can offset approximately €15,000 to €25,000 in annual electricity costs, depending on local solar conditions and consumption patterns. The financial benefits of solar farming extend beyond mere cost reduction, as excess power can be sold back to the grid through feed-in tariffs or power purchase agreements.
Most European countries offer attractive compensation rates for solar-generated electricity, ranging from €0.08 to €0.15 per kilowatt-hour. With an average 1-acre installation producing between 200,000 and 250,000 kWh annually, this can translate to additional income of €16,000 to €37,500 per year. The exact figures depend on factors such as local irradiance levels, system efficiency, and specific grid connection agreements.
Operating costs remain relatively low, typically ranging from €1,000 to €2,000 annually for maintenance and insurance. When combined with various EU and national-level incentives, most installations achieve complete return on investment within 6-8 years, while continuing to generate savings and income for 20+ years.
Agricultural Productivity Gains
The integration of solar panels with agricultural land creates remarkable opportunities for enhanced farm productivity and diversified income streams. Known as agrivoltaics, this innovative approach allows farmers to maintain their agricultural operations while generating clean energy, effectively maximizing land use efficiency.
Studies across European farms have shown that certain crops actually benefit from the partial shade provided by solar panels. Leafy vegetables, berries, and various root crops have demonstrated increased yields when grown under solar arrays, particularly during intense summer heat. The panels create a microclimate that helps retain soil moisture and protect plants from extreme weather conditions.
Farmers implementing this dual-use strategy typically see a 60-80% reduction in water consumption due to decreased evaporation, while maintaining comparable or improved crop yields. The additional income from solar power generation provides a stable revenue stream, helping to offset seasonal fluctuations in agricultural income.
Moreover, the infrastructure of solar installations can support advanced farming techniques, such as rainwater harvesting systems and automated irrigation. This technological integration enables precise resource management and improved crop monitoring, leading to more sustainable and efficient farming practices.
For livestock farmers, the solar arrays can provide valuable shade for grazing animals, particularly sheep, which naturally help maintain vegetation around the panels.
European Support and Regulations
The European Union strongly supports the development of solar farms through various policies and financial mechanisms. The Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) sets ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption, with solar playing a crucial role in achieving these goals. For 1-acre solar installations, project developers can access funding through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and specific national incentive schemes.
Member states offer different support mechanisms, with feed-in tariffs and premium payments being common. France, for instance, provides enhanced tariffs for agricultural solar projects, while Germany’s EEG law ensures stable returns through guaranteed grid access and fixed compensation rates. The Netherlands offers the SDE++ scheme, supporting both small and medium-scale solar installations.
Compliance requirements include environmental impact assessments, grid connection permits, and land-use authorizations. Projects must adhere to the EU’s Habitats Directive and Birds Directive when located near protected areas. Local authorities typically require detailed documentation on soil protection measures and biodiversity management plans.
The European Green Deal further strengthens support for solar farms by streamlining permitting processes and providing technical assistance through initiatives like InvestEU and the Just Transition Mechanism. Developers can also benefit from standardized equipment certifications under the EU’s Ecodesign Directive, ensuring quality and performance standards across the continent.
For optimal project development, engaging with local renewable energy associations and utilizing the EU’s technical assistance facilities is recommended. These resources help navigate regulatory requirements while maximizing available support mechanisms.
A one-acre solar farm represents a significant opportunity for European landowners to contribute to sustainable energy production while securing long-term financial benefits. With the potential to generate between 150 and 250 MWh annually, these installations can power numerous households while reducing carbon emissions substantially. The combination of decreasing installation costs, improving technology efficiency, and robust government incentives makes this an ideal time to invest in solar farming. Whether you’re a farmer looking to diversify income streams or a business seeking to enhance sustainability credentials, solar farms offer a proven path forward. Take the first step by consulting with local solar experts, reviewing regulatory requirements, and developing a comprehensive implementation plan. By acting now, you can join Europe’s growing network of clean energy producers while securing your energy future.
Leave a Reply